The skin is a highly specialized organ that acts as a physical, chemical, microbiological, and immunological barrier between the body and the external environment. This function is essential for cutaneous homeostasis, regulating transepidermal water loss (TEWL) and limiting the penetration of chemical substances, microorganisms, and environmental factors.
From a protective perspective, the skin barrier limits the penetration of potentially harmful external agents, including chemical substances, microorganisms, and environmental factors. This function is based on the compact organization of corneocytes, the intercellular lipid matrix, and the maintenance of an acidic environment that hinders the colonization of pathogenic microorganisms.
In addition, it regulates skin hydration by retaining water in the stratum corneum through epidermal lipids and natural moisturizing factors; its disruption increases TEWL and reduces skin water content.
Cutaneous homeostasis refers to the skin’s ability to maintain a stable functional state in response to internal and external stimuli. This stability depends on the coordinated interaction of the physical, chemical, microbiological, and immunological barriers, enabling controlled adaptive responses and preserving long-term skin functionality.
Disruption of the skin barrier is associated with dehydration, increased sensitivity, and low-grade inflammation, while its integrity forms the basis of functionally balanced and resilient skin.
Structural organization of the skin barrier function.
The skin barrier function mainly depends on the structural organization of the epidermis, particularly the stratum corneum, which regulates skin permeability and limits both transepidermal water loss and the entry of external agents. This architecture, described as the “brick and mortar” model, in which corneocytes represent the structural elements (“bricks”) and epidermal lipids form the continuous matrix (“mortar”), is critical for barrier integrity, as it determines both mechanical resistance and functional effectiveness.
Cellular cohesion, regulated by corneodesmosomes and tight junctions in the underlying epidermal layers, enables an appropriate balance between cellular renewal and structural continuity. This balance is key to maintaining a functional barrier, as accelerated or disorganized desquamation compromises stratum corneum continuity and increases skin permeability.
Tight junctions in the underlying epidermal layers contribute to barrier function by limiting the passage of solutes and reinforcing epidermal compartmentalization. Dysfunction of these junctions is associated with increased skin permeability and chronic inflammation.
The structural organization of the stratum corneum and the underlying epidermal layers is essential for maintaining the skin barrier and hydration. Any alteration in this architecture compromises the skin’s ability to preserve its physiological balance.
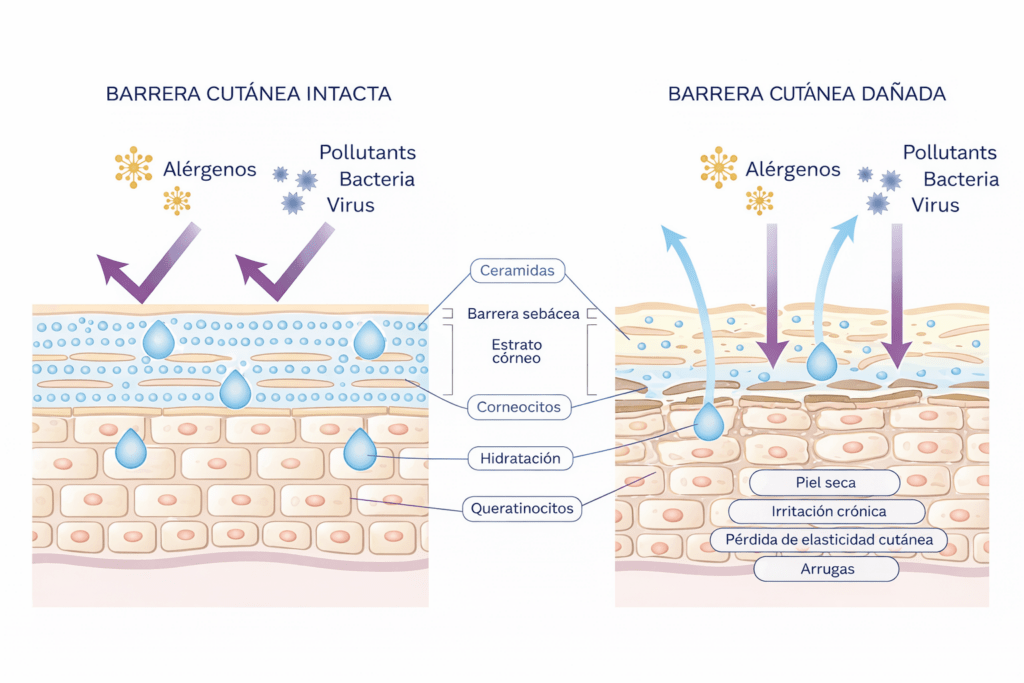
Skin Hydration and Barrier Function: A Bidirectional Relationship
Hydration as a Result of an Intact Barrier
Skin hydration is a direct consequence of proper epidermal barrier function. An intact barrier limits transepidermal water loss and helps maintain adequate water content in the stratum corneum, which is essential for skin functionality and elasticity.
This balance mainly depends on the integrity of the intercellular lipid matrix and natural moisturizing factors (NMF), whose proper organization enables the skin to maintain hydration even under changing environmental conditions.
Transepidermal Water Loss (TEWL) as a Functional Indicator
Transepidermal water loss (TEWL) is considered one of the main functional indicators of skin barrier status. Elevated TEWL values reflect increased epidermal permeability and, therefore, disruption of barrier function, even before visible clinical signs of dryness or skin damage appear.
Consequences of Barrier Disruption: Dehydration, Sensitivity, and Inflammation
When barrier function is compromised, increased TEWL leads to a progressive loss of hydration in the stratum corneum, reducing skin flexibility and affecting epidermal differentiation, which further weakens the barrier.
In addition, a disrupted barrier facilitates the penetration of external agents, activating immune responses that increase skin sensitivity and low-grade inflammation, thereby perpetuating damage. This disruption also affects the skin microbiota by altering pH and lipid composition, promoting local inflammatory responses.
The Four Functional Pillars of the Skin Barrier
Skin barrier function depends on the coordinated interaction of four pillars: physical, chemical, microbiological, and immunological. The integrity of these systems is essential for maintaining skin homeostasis and hydration.
Alterations in any of these pillars compromise overall barrier function, even when other components remain intact, which explains the complexity of disruption and repair processes.
HYSICAL BARRIER The main structure responsible for controlling skin permeability. It is primarily formed by the stratum corneum, composed of compacted corneocytes and an organized intercellular lipid matrix. Its integrity limits transepidermal water loss and hinders the entry of external agents. | CHEMICAL BARRIER Determined by the acid mantle, epidermal lipid content, and natural moisturizing factors (NMF). The slightly acidic pH regulates enzymatic activity involved in lipid synthesis, physiological desquamation, and the maintenance of stratum corneum cohesion. |
IMMUNOLOGICAL BARRIER It includes resident cells of the epidermis and dermis, such as keratinocytes, Langerhans cells, and cutaneous lymphocytes. It enables the detection of structural alterations or external agents and activates controlled responses aimed at barrier defense and repair. | MICROBIOLOGICAL BARRIER Formed by the resident skin microbiota, which helps preserve physiological pH, limit pathogen colonization, and modulate local inflammatory responses. Its balance is closely linked to the integrity of the physical and chemical barriers. |
Cosmetic Strategies to Restore Barrier Function and Hydration
PromoCare® CRM Complex
PromoCare® CRM Complex is a biomimetic ceramide complex designed to provide long-lasting hydration, effective barrier repair, and improved transdermal absorption of water-soluble actives in cosmetic formulations. It is compatible with all types of systems and shows high stability at both high and low temperatures. It is suitable for a wide range of skincare products, including toners, moisturizing lotions, serums, masks, and facial cleansers.
INCI: Water, Butylene Glycol, Hydrogenated Lecithin, Caprylic/Capric Glycerides Polyglyceryl-10 Esters, Pentylene Glycol, Ceramide AP, Ceramide NG, Ceramide NP, Ceramide EOS
In vivo study (21 days): Use of 2% PromoCare® CRM Complex.
- Result: Sustained reduction in transepidermal water loss over time, confirming its moisturizing efficacy and its ability to reinforce barrier function.
CS-LCC Aurora Plus
CS-LCC Aurora Plus (Liquid Crystal Ceramide Pearlescent) is an ingredient based on cholesteric liquid crystals that combines ceramide NP and lecithin. It is designed to reinforce skin barrier function, improve hydration, and provide a stable pearlescent effect in formulations. Its liquid crystal structure contributes to skin comfort and a fresh, lightweight texture, with good stability across different cosmetic systems.
INCI: Water, Glycerin, Diethoxyethyl Succinate, Butylene Glycol, Polyglyceryl-3 Cocoate, Ceramide NP, Hydrogenated Lecithin, Ethylhexylglycerin, Hydroxyacetophenone, Lecithin.
In vivo study (2 weeks, n = 23). Use of 5% CS-LCC Aurora Plus.
- Result: 26.4% improvement in skin hydration, assessed through the reduction of transepidermal water loss (TEWL) after two weeks of application (three times daily).
- Skin elasticity: 3.8% increase in CoR value, indicating improved skin elasticity after the same period of use.
In vitro study.
- Anti-inflammatory activity: after 24 hours of treatment with 0.1% CS-LCC Aurora Plus, a 71% inhibition of TNF-α-induced NF-κB activation was observed, confirming a significant anti-inflammatory effect at the cellular level.
KTP1-Filagreen
 KTP1-Filagreen is the first cosmetic ingredient to incorporate filaggrin, a key structural protein involved in strengthening skin barrier function. Filaggrin increases keratinocyte resistance by aggregating keratin fibers, thereby reinforcing the architecture of the stratum corneum. After fulfilling its structural role, it is physiologically degraded into Natural Moisturizing Factors (NMF), contributing to the maintenance of skin balance.
KTP1-Filagreen is the first cosmetic ingredient to incorporate filaggrin, a key structural protein involved in strengthening skin barrier function. Filaggrin increases keratinocyte resistance by aggregating keratin fibers, thereby reinforcing the architecture of the stratum corneum. After fulfilling its structural role, it is physiologically degraded into Natural Moisturizing Factors (NMF), contributing to the maintenance of skin balance.
Thanks to its KTP delivery system (Protein Transduction Domain), KTP1-Filagreen facilitates the intracellular penetration of filaggrin into keratinocytes, overcoming the typical limitation of hydrophilic proteins in topical applications.
INCI: Water, Lecithin, Butylene Glycol, sh-Oligopeptide-194, sh-Polypeptide-170, Disodium EDTA, Sodium Ascorbyl Phosphate, Polysorbate 20, 1,2-Hexanediol
In vitro studies (HaCaT cells).
- Skin penetration: penetration rate of 67.5%, compared to 9.6% for filaggrin without the KTP system (p < 0.01).
- Cellular proliferation: increase of up to 197.6% at 10 µg/mL (p < 0.01).
- Wound healing: increase in wound closure of up to 91.5% at 10 µg/mL (p <0.01).
Ex vivo studies (IL-4/IL-13–induced atopic skin model).
- Filaggrin expression: 49.85% increase compared to the stimulated group.
- NMF production: 101.9% increase in caspase-14 expression, a key enzyme in NMF generation, associated with the recovery of barrier function.
These results support the use of KTP1-Filagreen as an effective ingredient for strengthening barrier function at the keratinocyte level, making it especially suitable for formulations intended for dry, sensitive, or barrier-impaired skin.
Phyto Collagen (PD)

Phyto Collagen (PD) is a naturally derived ingredient obtained from Tremella fuciformis, rich in polysaccharides and extensin-type glycoproteins that are structurally similar to collagen. Its low molecular weight promotes the formation of a flexible film on the skin, helping to improve comfort, skin elasticity, and barrier function.
INCI: Water, Propanediol, Tremella Fuciformis (Mushroom) Extract
In vitro studies.
- Anti-aging activity: at a concentration of 1%, Phyto Collagen (PD) showed a 20.8% inhibition of MMP-1 activity in human dermal fibroblasts exposed to UVA radiation (p<1, a key enzyme involved in collagen degradation and loss of elasticity.
- Water retention capacity: in comparative tests at 10%, Phyto Collagen (PD) showed superior water-holding capacity compared to water and glycerin, maintaining moisture content for a longer period of time.
Ex vivo studies.
- Skin hydration: an emulsion containing 5% Phyto Collagen (PD) increased AQP3 expression by 56.7%, a key protein involved in water transport between epidermal cells.
- Barrier function: 18.75% increase in filaggrin expression, associated with enhanced production of Natural Moisturizing Factors (NMF).
- Elasticity: 21.6% increase in elastin expression in the dermis, reinforcing skin structure and elasticity.
Hydra Biotics

Hydra Biotics is an ingredient derived from floral probiotics isolated from Jeju hydrangea, featuring a proprietary registered strain and a pending patent. It has been developed to strengthen skin barrier function and soothe sensitive skin. Its activity is based on probiotic metabolites that contribute to skin pH balance, barrier integrity, and overall skin comfort.
INCI: Water, Lactobacillus Ferment Lysate, Butylene Glycol, 1,2-Hexanediol
In vitro study
- pH regulation and barrier function: Hydra Biotics contains 4000pm of organic acids (lactic, citric, and acetic acids), which contribute to maintaining physiological pH and strengthening the natural antimicrobial barrier. >
- Epidermal lipid synthesis: significant increase in epidermal ceramides in keratinocytes, including Dh C18:0 and Dh C24:0, key structural lipids of the stratum corneum.
- Soothing / anti-pruritic effect: dose-dependent reduction in TRPV-1 expression (a marker of skin itching):
- −8,07 % at 1 %
- −21,22 % at 5 %
- −26,59 % at 10 %
Skin Barrier Enhacer
Skin Barrier Enhancer is an active ingredient designed to strengthen skin barrier function by stimulating endogenous ceramide biosynthesis through the regulation of serine palmitoyltransferase (SPT), a key enzyme in epidermal lipid formation. Its approach goes beyond surface hydration, promoting structural and functional improvement of the barrier.
The complex combines selected botanical extracts (Eucalyptus globulus leaf extract, Panax ginseng root extract, and Chenopodium quinoa seed extract) with synergistic activity aimed at reinforcing the barrier, protecting against external aggressors, and soothing sensitive or compromised skin.*
INCI: Water, Butylene Glycol, Glycerin, Eucalyptus Globulus Leaf Extract, Panax Ginseng Root Extract, Chenopodium Quinoa Seed Extract, 1,2-Hexanediol, Ethylhexanediol
In vitro studies
- Ceramidase inhibition: treatment with Skin Barrier Enhancer dose-dependently reduced ceramidase activity, minimizing epidermal ceramide degradation.
- SPT stimulation: at concentrations of 1–5%, a significant increase in SPT expression was observed (p < 0.01), associated with enhanced ceramide synthesis.
- Lipid biosynthesis: total ceramide content increased by up to 73.7% compared to the control, confirmed by LC-MS/MS analysis.
- Anti-inflammatory activity: dose-dependent inhibition of nitric oxide (NO) synthesis in LPS-stimulated macrophages (p < 0.01).
In vivo studies
- Transepidermal water loss (TEWL): following induced exfoliation, application of an emulsion containing 3% Skin Barrier Enhancer produced a significant reduction in TEWL at 30 and 60 minutes, confirming rapid reinforcement of barrier function.
- Skin lipid content: after two weeks of use, an increase of 98% in squalene and 43% in cholesterol in the stratum corneum was observed, key indicators of a strengthened lipid barrier.
Skin barrier function constitutes a complex and dynamic system whose integrity is essential for maintaining the skin’s physiological balance. Beyond its role as a protective structure, the barrier acts as an integrated regulator that brings together physical, chemical, microbiological, and immunological components, determining the skin’s ability to adapt to external stimuli and preserve long-term functionality.
From a cosmetic perspective, restoring and reinforcing barrier function requires formulation strategies based on well-defined biological mechanisms. The combination of ingredients that act on the stratum corneum lipid matrix, epidermal differentiation, pH balance, and interactions with the skin microbiota makes it possible to address the skin barrier in an integrated manner, avoiding reductionist approaches.
In this context, selecting active ingredients supported by specific efficacy studies and appropriate experimental models becomes a key factor in developing cosmetic products with a technical, coherent approach aligned with real skin needs.
At Ismael Quesada Personal Care, we provide our clients with detailed technical information and specialized support for selecting ingredients aimed at strengthening skin barrier function.
If you would like to receive further information on these actives or explore their application in new formulations, please contact our team. We will be pleased to support you in the development of your upcoming projects.
References
- Fluhr, J. W., Darlenski, R., & Lachmann, N. (2012). Transepidermal water loss and skin barrier function. Clinics in Dermatology, 30(3), 263–272. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16761956/
- Fluhr, J. W., Muguet, V., & Christen-Zaech, S. (2025). Restoring skin hydration and barrier function: Mechanistic insights into basic emollients for xerosis cutis. International Journal of Dermatology, 64(Suppl. 1). https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/40231699/
- Proksch, E., Brandner, J. M., & Jensen, J.-M. (2008). The skin: An indispensable barrier. Experimental Dermatology, 17(12), 1063–1072. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19043850/
- Elias, P. M. (2005). Stratum corneum defensive functions: An integrated view. Journal of Investigative Dermatology, 125(2), 183–200. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0022202X15527934
- Rawlings, A. V., & Harding, C. R. (2004). Moisturization and skin barrier function. Dermatologic Therapy, 17(Suppl. 1), 43–48 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14728698/

